IJERPH, Free Full-Text
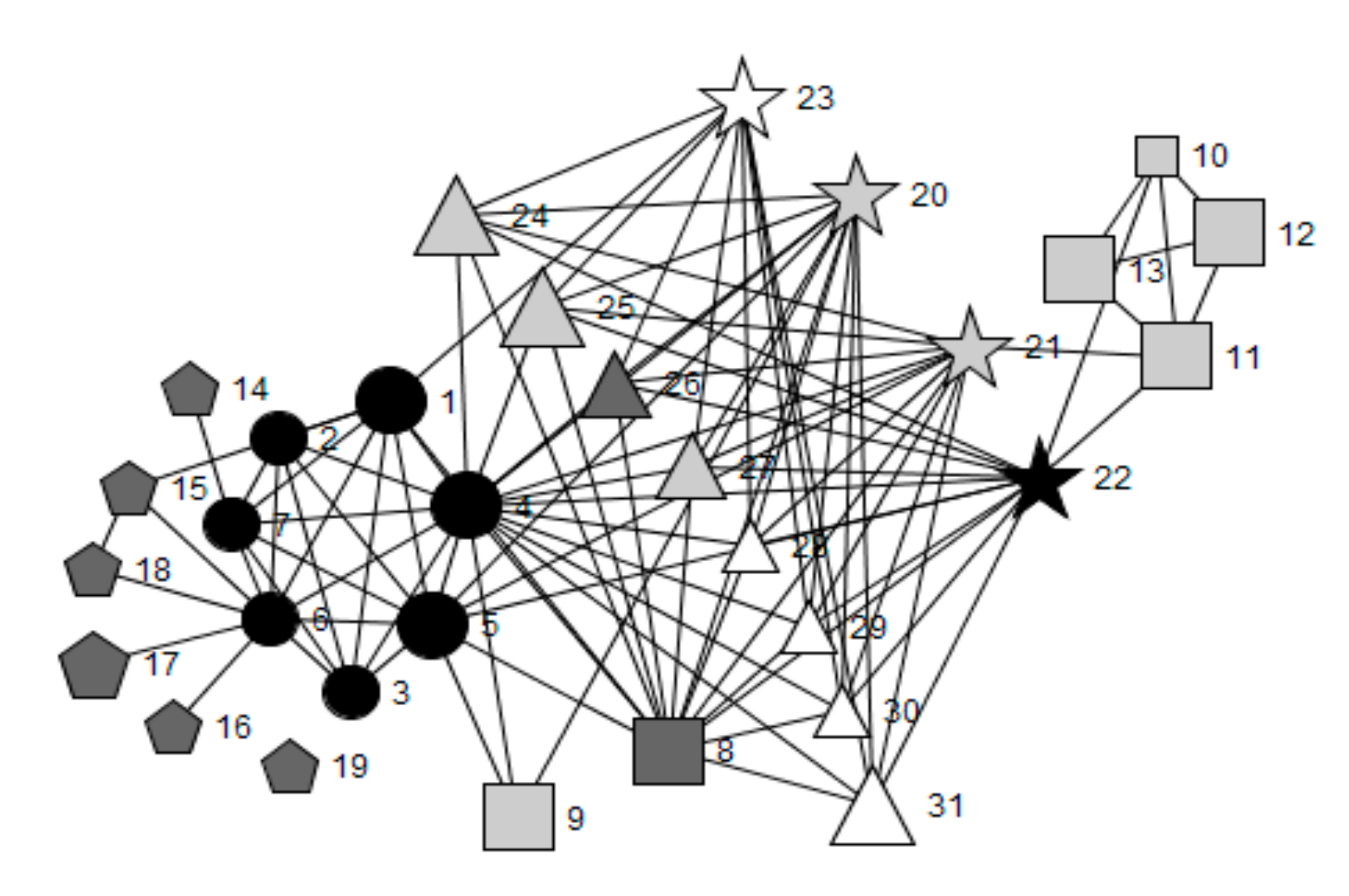
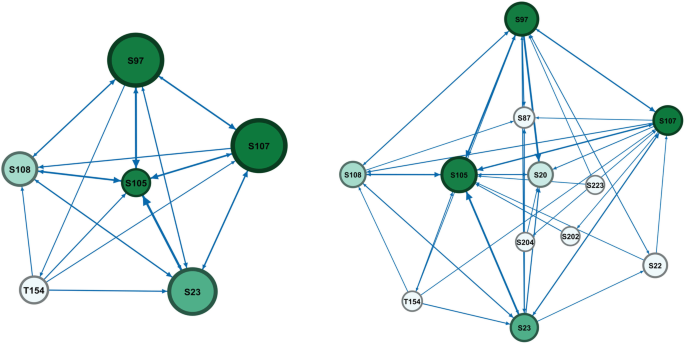
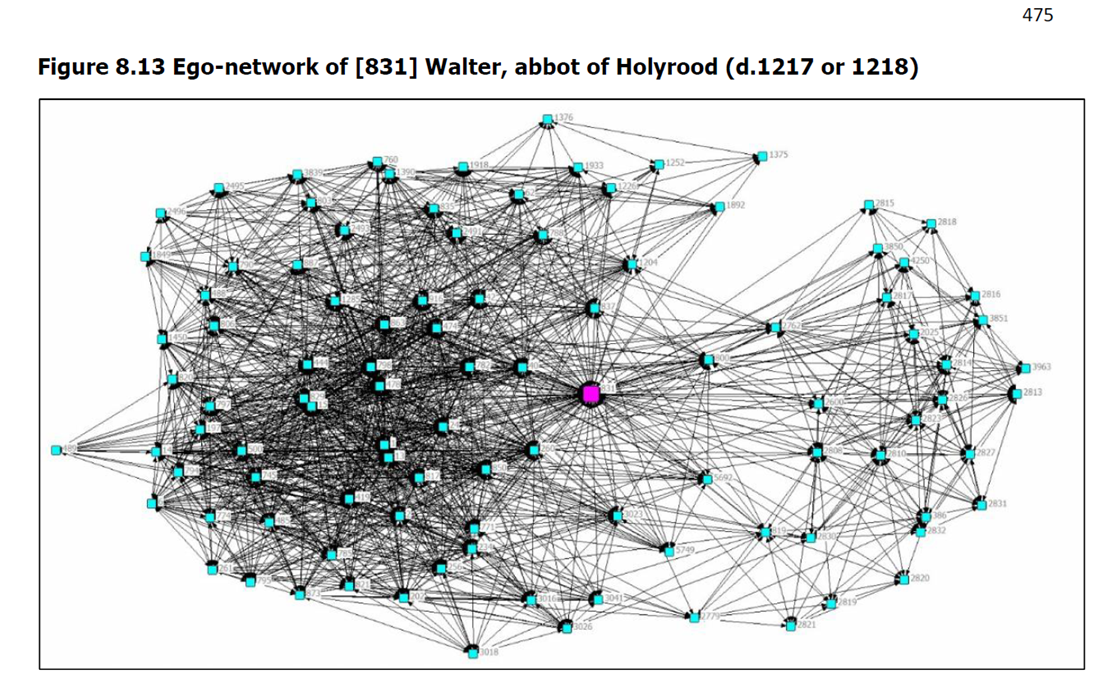
Challenges in changing school system functioning to orient them towards health are commonly underestimated. Understanding the social interactions of school staff from a complex systems perspective may provide valuable insight into how system dynamics may impede or facilitate the promotion of health and wellbeing. Ego social network analysis was employed with wellbeing leads within four diverse case study schools to identify variability in embeddedness of health and wellbeing roles. This variation, as well as the broader context, was then explored through semi-structured qualitative interviews with school staff and a Healthy Schools Coordinator, sampled from the wellbeing leads’ ego-networks. Networks varied in terms of perceived importance and frequency of interactions, centrality, brokerage and cliques. Case study schools that showed higher engagement with health and wellbeing had highly organised, distributed leadership structures, dedicated wellbeing roles, senior leadership support and outside agencies embedded within school systems. Allocation of responsibility for wellbeing to a member of the senior leadership team alongside a distributed leadership approach may facilitate the reorientation of school systems towards health and wellbeing. Ego-network analysis to understand variance in complex school system starting points could be replicated on a larger scale and utilised to design complex interventions.

Images

IJERPH, Free Full-Text, impact nursing
IJERPH, Free Full-Text

IJERPH, Free Full-Text, Pva
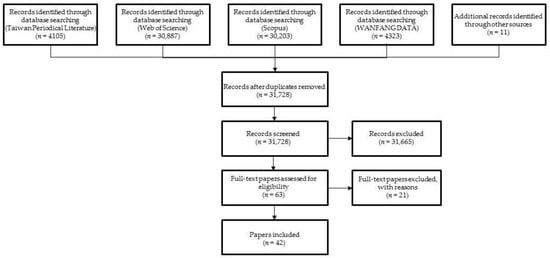
IJERPH, Free Full-Text

International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
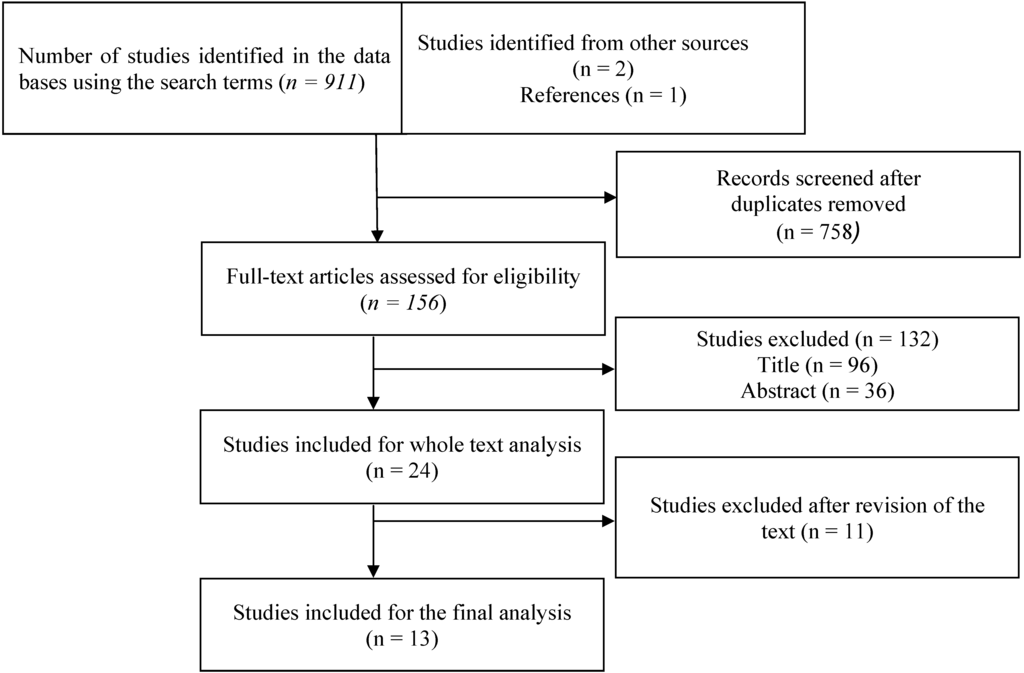
IJERPH, Free Full-Text
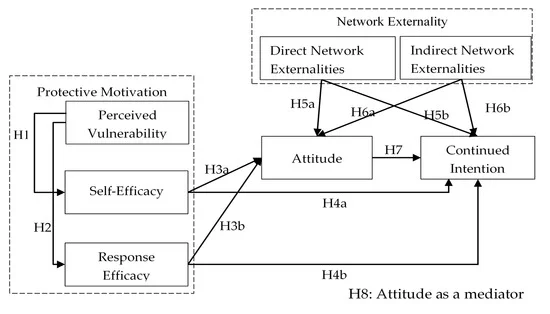
IJERPH, Free Full-Text, Chinese Calligraphy Brush
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
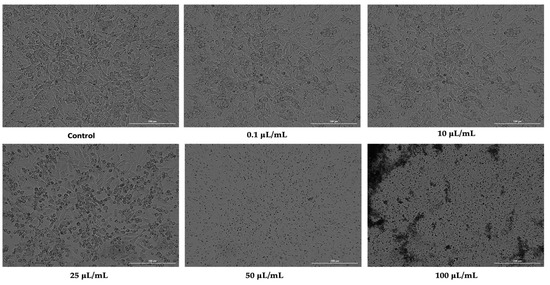
IJERPH, Free Full-Text, time control contabilidade
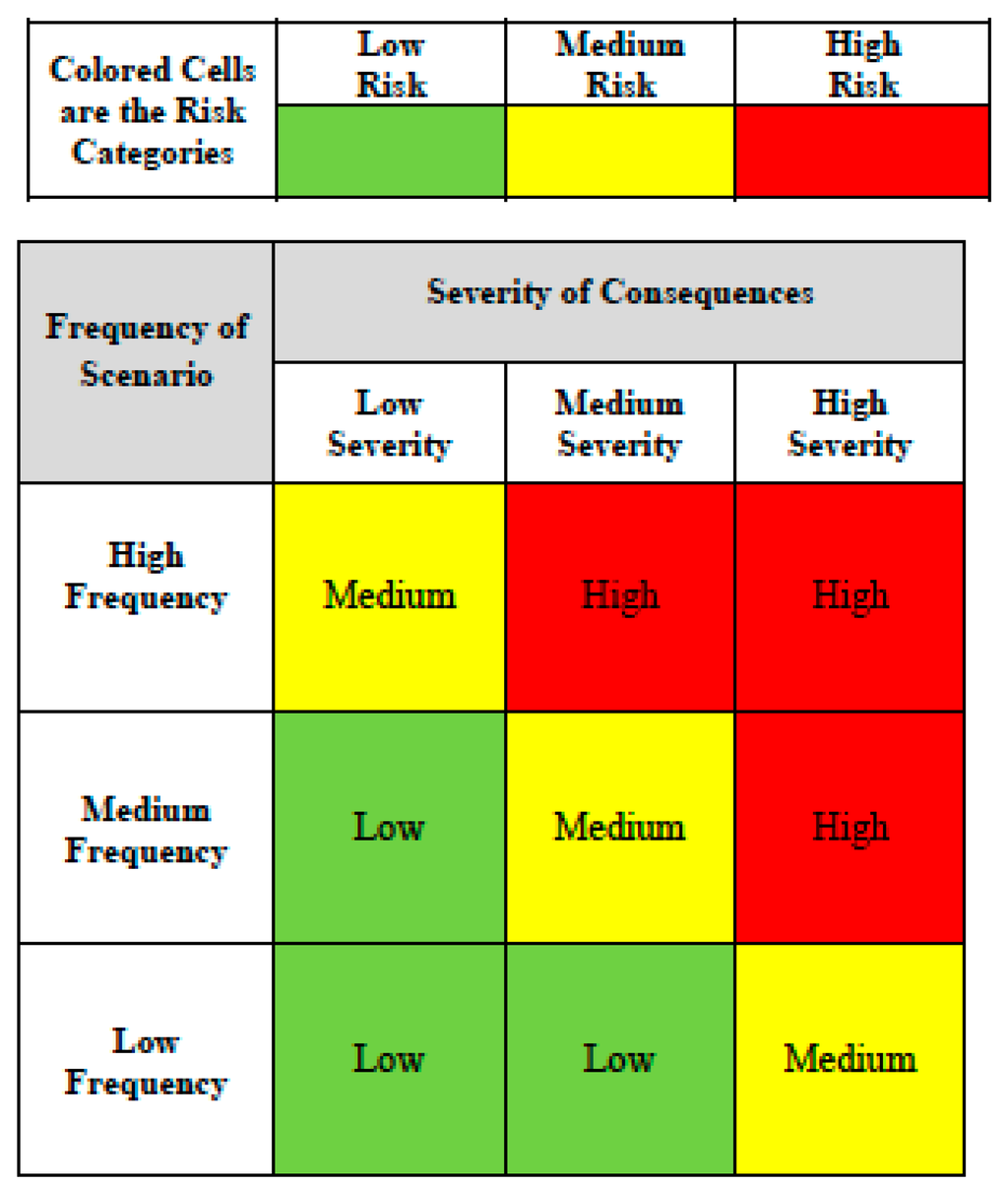
IJERPH, Free Full-Text, natural benefit