Marine ecosystem - Salinity, Temperature, Oxygen

Marine ecosystem - Salinity, Temperature, Oxygen: The physical and chemical properties of seawater vary according to latitude, depth, nearness to land, and input of fresh water. Approximately 3.5 percent of seawater is composed of dissolved compounds, while the other 96.5 percent is pure water. The chemical composition of seawater reflects such processes as erosion of rock and sediments, volcanic activity, gas exchange with the atmosphere, the metabolic and breakdown products of organisms, and rain. (For a list of the principal constituents of seawater, see seawater: Dissolved inorganic substances.) In addition to carbon, the nutrients essential for living organisms include nitrogen and phosphorus, which are minor constituents
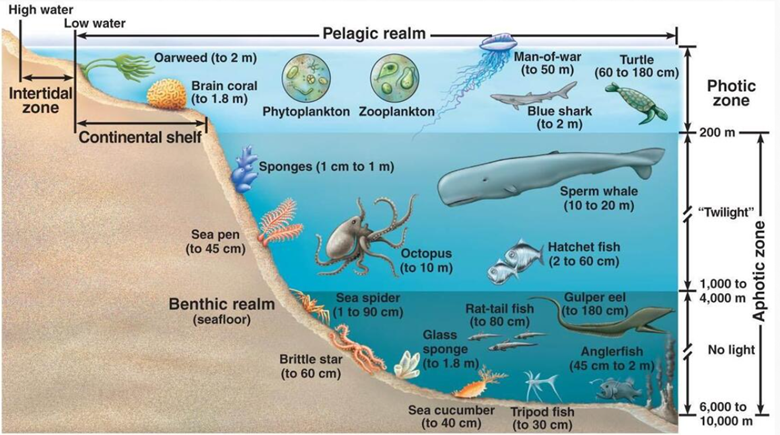
Marine ecosystem, complex of living organisms in the ocean environment. Marine waters cover two-thirds of the surface of the Earth. In some places the ocean is deeper than Mount Everest is high; for example, the Mariana Trench and the Tonga Trench in the western part of the Pacific Ocean reach

Marine ecosystem - Salinity, Temperature, Oxygen
Aquatic Ecosystems - Welcome to Dr. Suris Science Class!
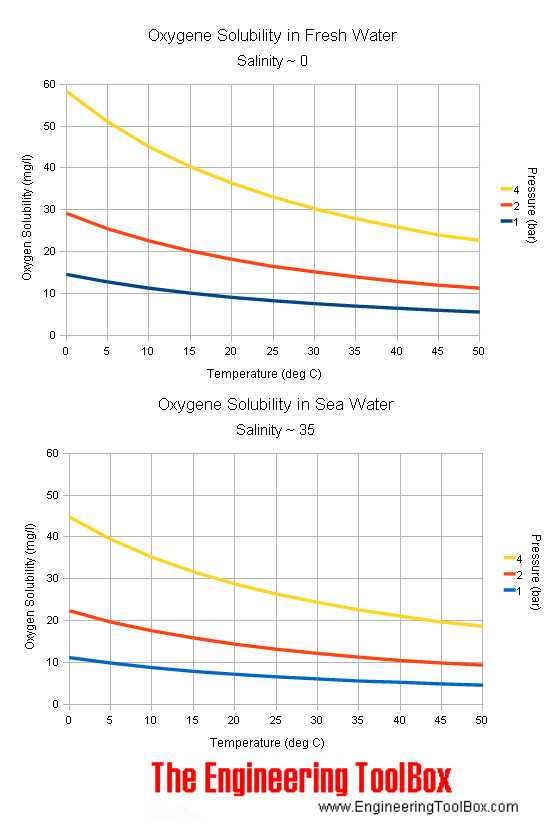
Oxygen - Solubility in Fresh and Sea Water vs. Temperature

Marine ecosystem - Salinity, Temperature, Oxygen
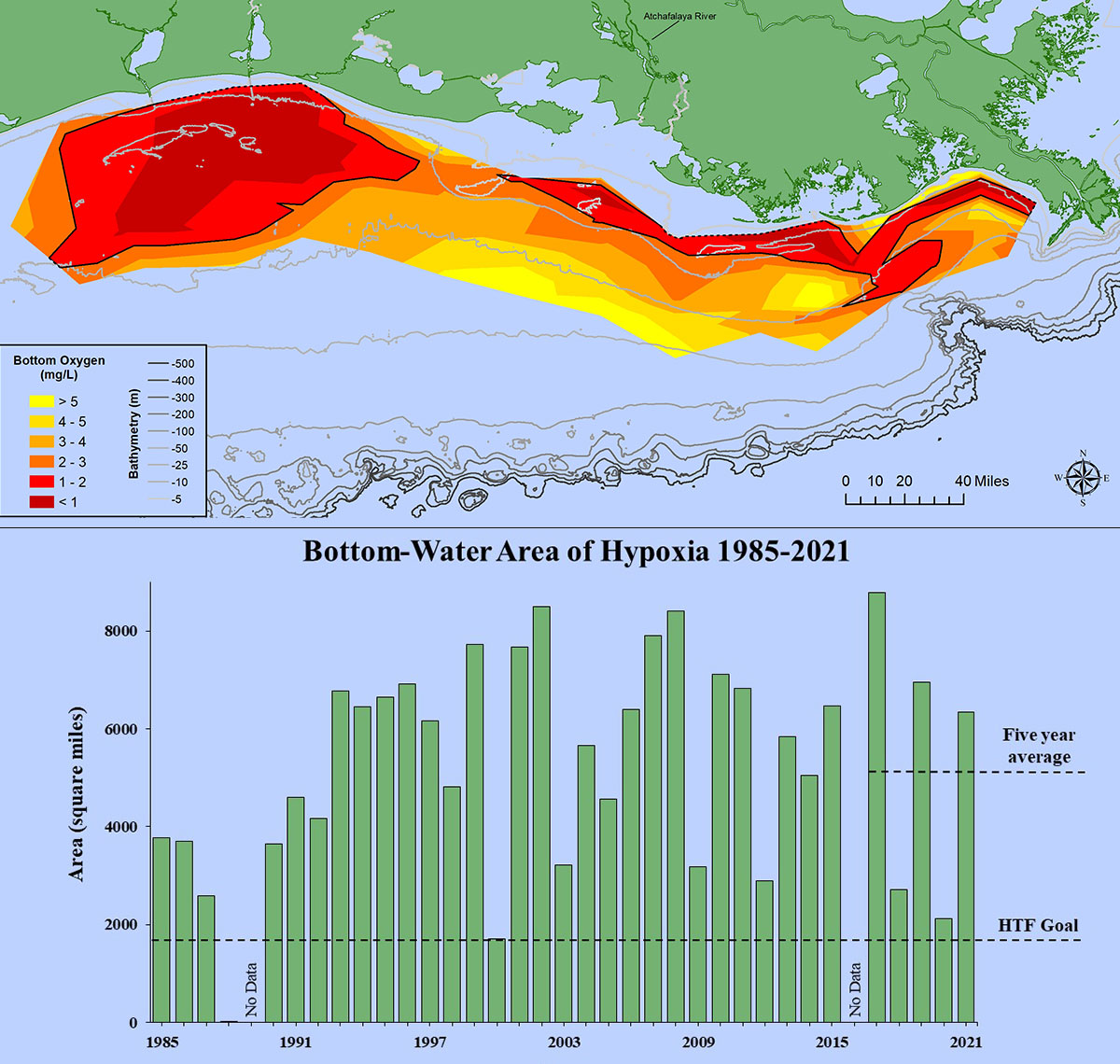
Dealing with Dead Zones: Hypoxia in the Ocean
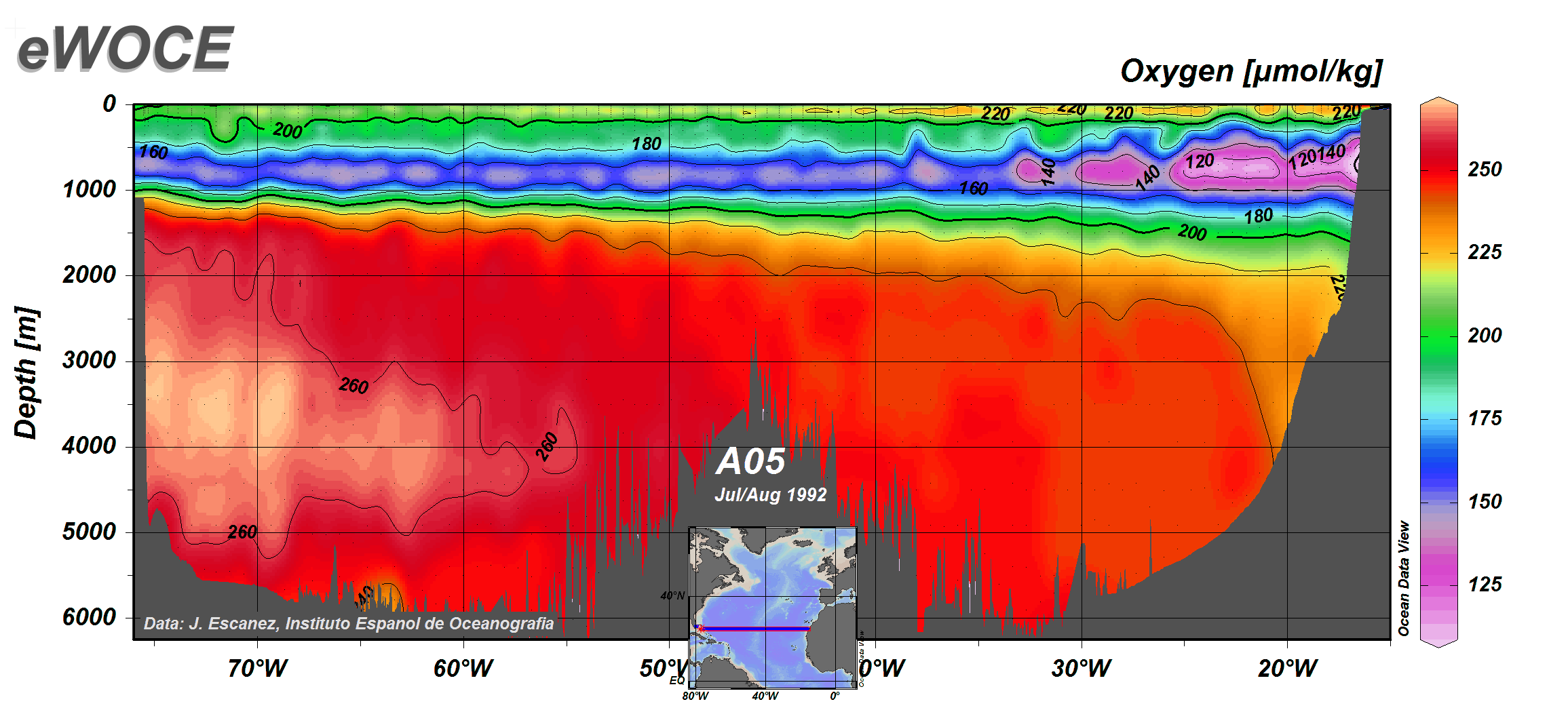
5.4 Dissolved Gases: Oxygen – Introduction to Oceanography

Pycnocline - Wikipedia
How Does Climate Change Affect the Ocean?
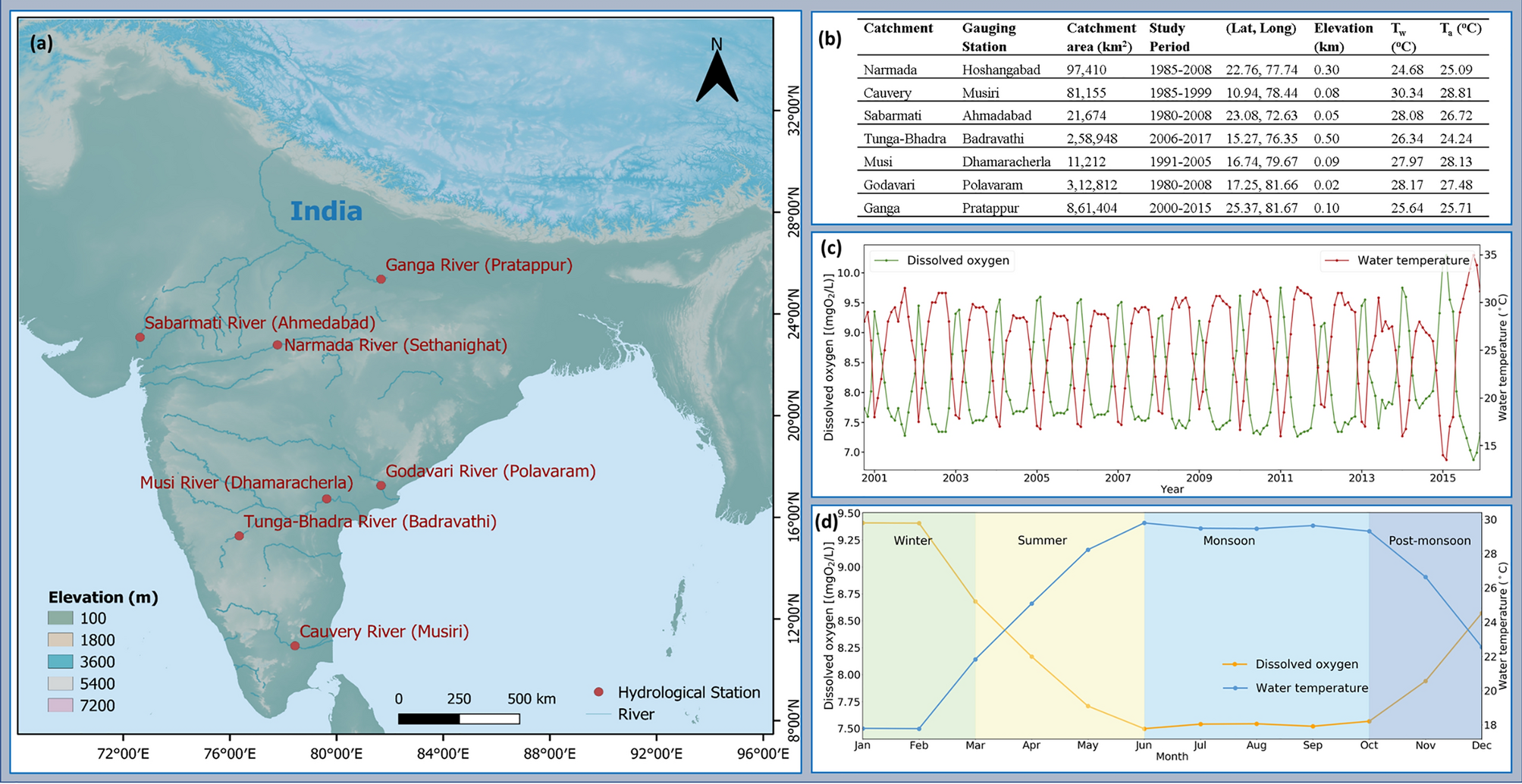
Impact of climate change on river water temperature and dissolved oxygen: Indian riverine thermal regimes

Marine water parameters and their impact on ocean life

Marine ecosystem - Salinity, Temperature, Oxygen

Dissolved Oxygen - Environmental Measurement Systems
The relationship between seawater oxygen concentration and impact