PDF] The risks of gastrointestinal injury due to ingested magnetic

It is proposed that if magnet ingestion is suspected, early endoscopic or surgical retrieval is mandatory and Appropriate, rapid surgical intervention is indicated. Accidental ingestion of foreign bodies is a common problem in children. Magnetic bead toys are hazardous, having potentially lethal consequences if ingested. These magnets conglomerate in different segments of bowel, causing pressure necrosis, perforation and/or fistula formation anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract. A clinical diagnostic pitfall is that the appearance on the initial abdominal radiograph may be misinterpreted by the uninitiated as a single metallic object without any intervening intestinal wall. Symptoms do not occur until complications have developed, and even then, unless magnet ingestion is suspected, treatment may initially be mistakenly expectant, as with any other foreign body. After observing a case of multiple magnet ingestion that led to the rapid onset of small-bowel inter-loop fistulas and peritonitis, we attempted to reproduce the likely sequence of events in a laboratory setting using fresh, post-mortem porcine bowel as an animal model and placing magnetic toy beads within the bowel lumen. Pressure-induced perforation appeared extremely rapidly, replicating the operative findings in two of our cases. We propose that if magnet ingestion is suspected, early endoscopic or surgical retrieval is mandatory. Appropriate, rapid surgical intervention is indicated. Laparoscopy offers a minimally invasive therapeutic option.

Pediatric Magnet Ingestion with delayed presentation
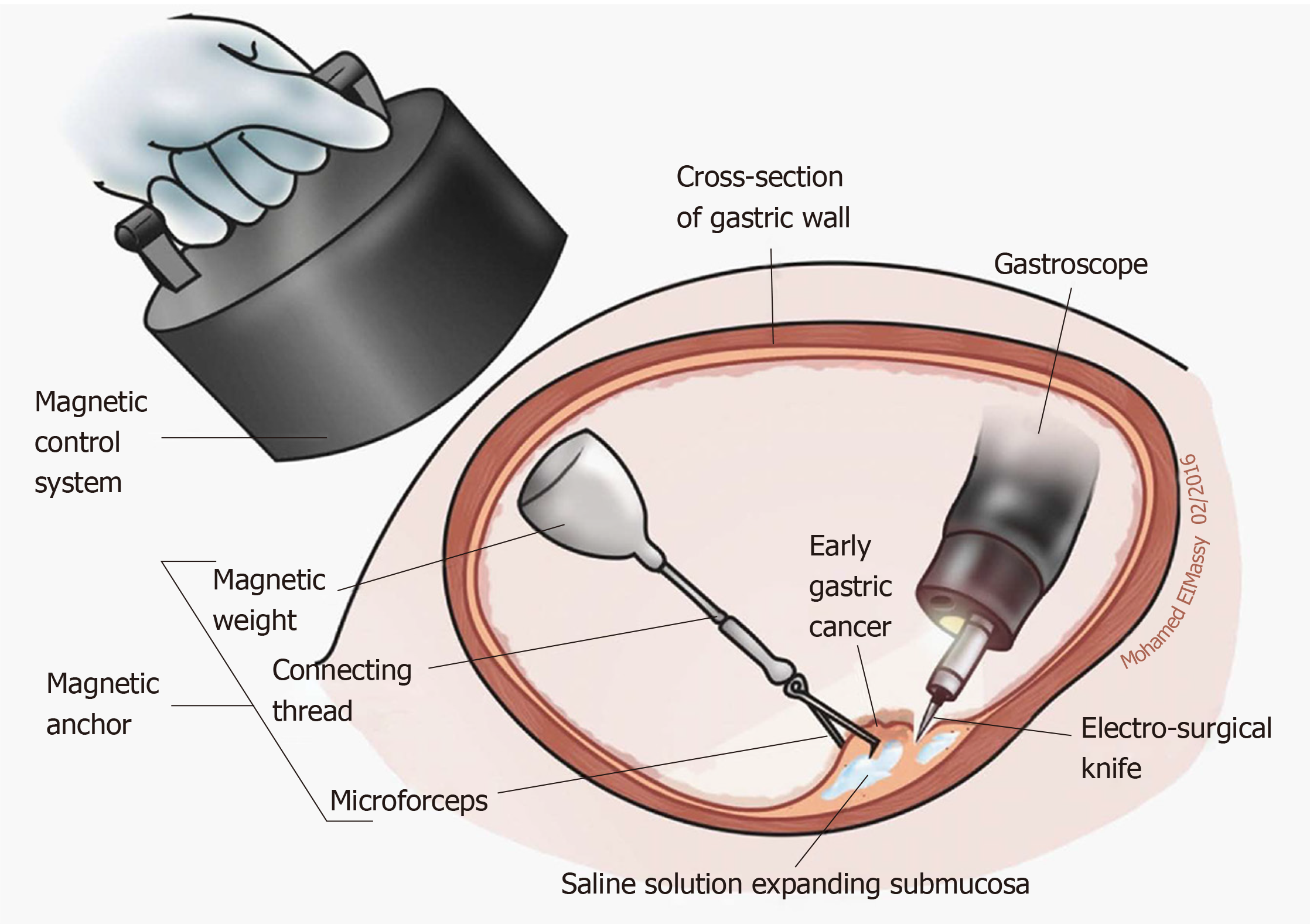
Endoscopic applications of magnets for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases
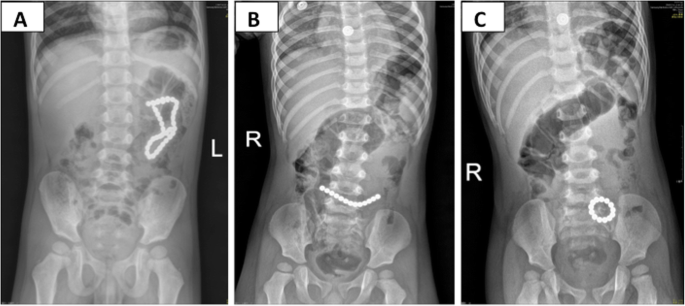
Multicenter investigation of pediatric gastrointestinal tract magnets ingestion in China, BMC Pediatrics

PDF) Pediatric Magnet Ingestion, Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention: A European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Position Paper

Laparoscopic assisted removal of multiple ingested magnetic foreign bodies in a child - ScienceDirect

Cureus, A Child With a Gastrocolic Fistula After Ingesting Magnets: An Unusual Complication

PDF) Ingested magnets and gastrointestinal complications

Management of multiple magnetic foreign body ingestion in pediatric patients, BMC Pediatrics
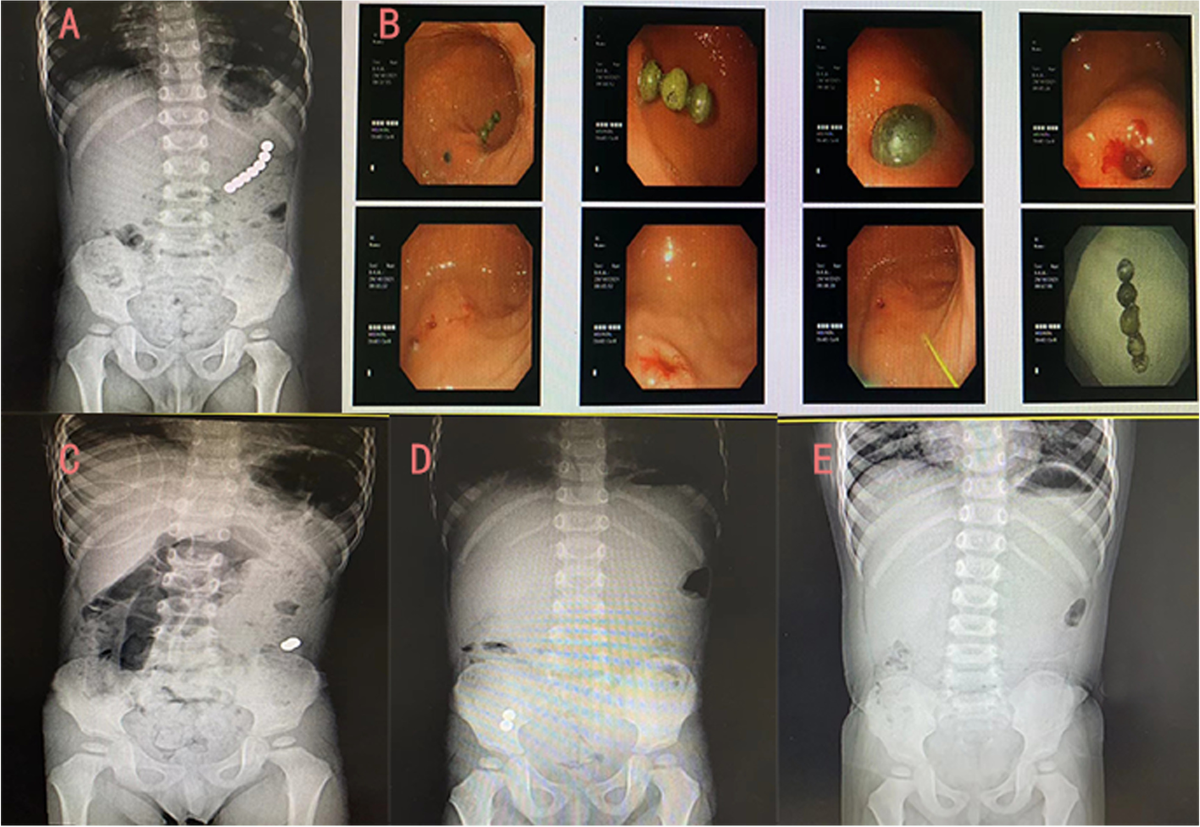
Management of multiple magnetic foreign body ingestion in pediatric patients, BMC Pediatrics
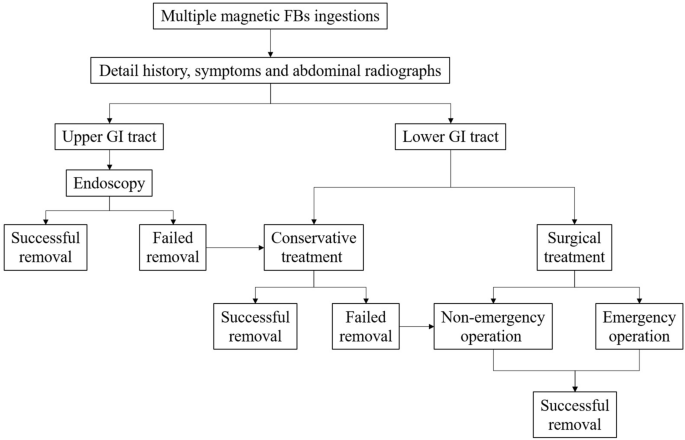
Multiple magnetic foreign body ingestion in pediatric patients: a single-center retrospective review
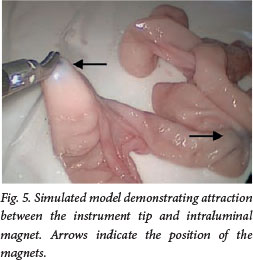
The risks of gastrointestinal injury due to ingested magnetic beads
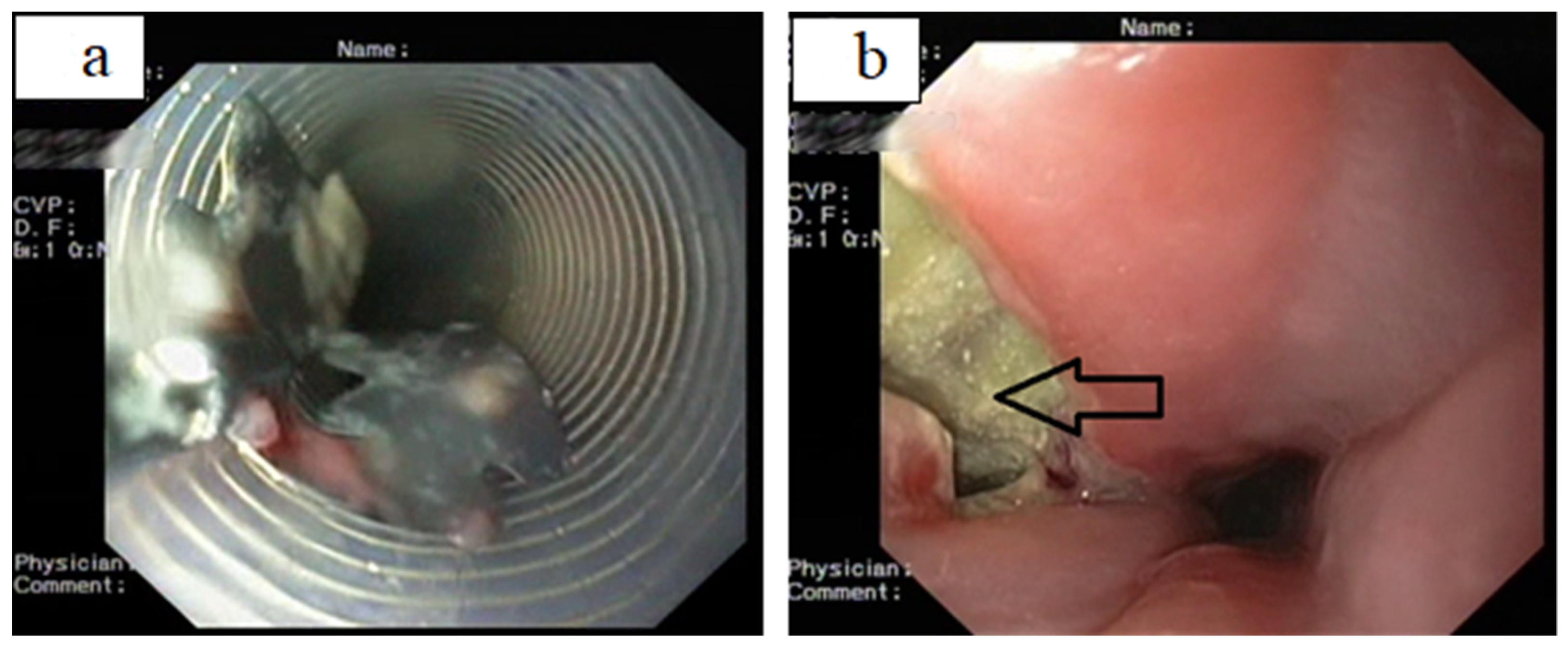
Gastroenterology Insights, Free Full-Text

GiKids - Magnet Ingestions
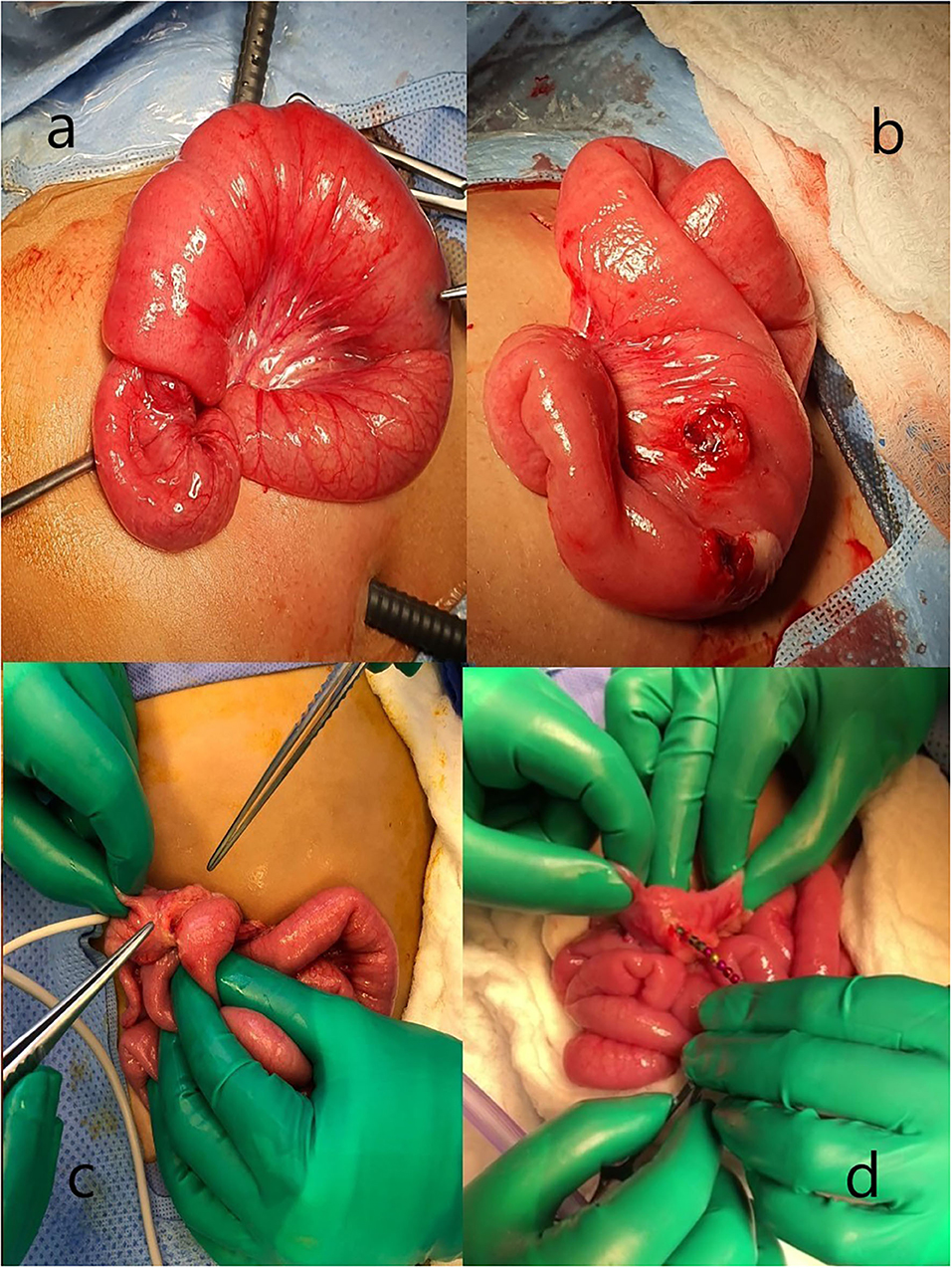
Frontiers Magnet Ingestion in Children Management Guidelines and Prevention







